Porter’s generic strategies are one of the most popular tools used when undertaking a competitive analysis in any industry. According to Porter (1985) companies can generally choose from two broad strategies, product differentiation or cost efficiency in broad market scope, or they may pursue product differentiation or cost efficiency strategies within a particular customer segment.
To put it simply, companies usually choose to maximise their profit through offering products or services in lower prices, or offering superior quality products or services for higher price. And this can be done for the whole business or for a particular customer segment.
A focus strategy “is defined by its emphasis on a single industry segment within which the orientation may be toward either low cost or differentiation” (Czinkota and Ronkainen, 2007, p.196).
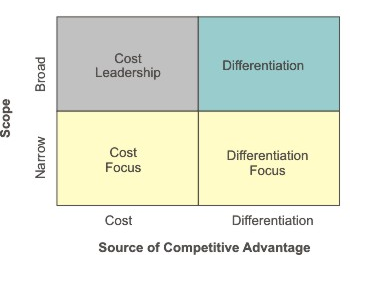
When pursuing a cost leadership strategy the company prices its products or services at a lower level than competition. Cost leadership strategy is associated with engagement in economies of scale and maintaining strict control of costs. Differentiation strategy, on the other hand, focuses marketing efforts on quality and uniqueness in relation to specific aspects of products or services.
There are many advantages product differentiation strategy provides to the business. Product differentiation strategy increases the level of customer loyalty dramatically by mentioning the statistical data according to which US consumer loyalty to a single brand varies from 30 percent in batteries up to 70 percent in cigarettes.
When conducting competitive analysis companies should seek following information: current strategy and future objectives of competitors, assumptions about the industry in which competitors believe, and strengths and weaknesses of competitors.
Example: Application of Porter’s Generic Strategies to Warner Bros.
According to Porter’s generic strategies differentiation in broad competitive scope marks the main competitive advantage of Warner Bros. The company engages in diversification in two levels: the quality of products and their delivery.
The quality of Warner Bros. films and entertainment products are diversified in a way that they attempt to stand out in terms of narrative and nature of ideas communicated through them, as well as, through attracting famous A-list actors and actresses. In terms of delivery and consumption, on the other hand, diversification is achieved through focus on digitisation of media and entertainment.
Moreover, some of the popular series produced by Warner Bros. such as The Bing Bang Theory, Two and Half Men, Mentalist, and Vampire Diaries have attracted acclaim of critics due to high levels of originality on various aspects of the show.